
Myasthenia gravis (MG) – a chronic autoimmune disorder, in which antibodies destroy the communication between nerves and muscle. And causes weakness in the skeletal muscles, muscles the body uses for movement. The degree of muscle weakness varies from person to person and the onset of myasthenia gravis can be sudden in some people. According to the Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America, it is estimated that 20 in 100,000 have myasthenia gravis and approximately 36,000 to 60,000 cases.
This article covers all the significant topics related to the myasthenia gravis such as the test cost, causes, symptoms, complications, and how to get tested for myasthenia gravis.
- Myasthenia gravis
- Myasthenia gravis causes
- Risk factor
- Symptoms of myasthenia gravis
- Complications
- Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis
- Is myasthenia gravis curable?
- Treatment for myasthenia gravis
- Lifestyle changes
- Provider locations
For our readers who are interested in knowing the myasthenia gravis test cost beforehand, we begin with that section.
How much does the myasthenia gravis test cost?
Myasthenia gravis test costs range around $319 in different labs and facilities across the U.S. No prior appointment is required. You may compare the price and order tests online, or visit the nearest lab during lab business hours. You will get the results in your email in 2-3 business days after completing the procedure. Doctor consultation is also available for any kind of medical advice or further treatment.
The following table shows the myasthenia gravis test provider and their price. You can know more and book the test now by clicking on the “Book Now” button. All the labs are certified and offer a network across the US.
Name of our Partner Labs | Book Online at Offer Price |
HealthLabs
| $319 |
Myasthenia gravis test cost with insurance
Many insurance companies in the U.S. cover all the vital tests. But the coverage offered by private health insurance companies and national health insurance programs like Medicare varies widely. Most of the health insurance policies cover myasthenia gravis test costs. However, you are recommended to check if your health insurance policy covers the myasthenia gravis test cost.
Our myasthenia gravis testing providers don’t accept any kind of health insurance policy. However, they can provide you with an itemized receipt containing all the details viz the name of the test, code of the test, and CPT code which is necessary for insurance reimbursement purposes.
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis or MG is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular condition that impairs communication between nerve and muscle. This prevents crucial muscle contractions from occurring and resulting in muscle weakness. This condition primarily affects the skeletal muscles or the muscles attached to bones and is responsible for skeletal movement. And it is not transmitted through intimate, sexual, or any other form of contact.
Currently, there is no cure for myasthenia gravis. However, with treatment, most people with MG lead relatively normal lives. The symptoms of MG tend to reach their peak in severity within 1 to 3 years of initial diagnosis. In nearly 15% of people with MG, the disease only affects the eyes and face. Although MG occurs regardless of age and gender it mostly affects women aged 20 to 40 and men aged 50 to 80. About 1 in 10 cases of myasthenia gravis (juvenile MG) occur in teenagers.
Myasthenia gravis causes
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder, generally caused by an autoimmune problem. An autoimmune disorder occurs when a person’s immune system attacks their body tissues. The immune system normally finds and destroys any unwanted invaders like bacteria, toxins, or viruses. But in the case of autoimmune disease, the antibodies circulate in the blood and attack healthy cells and tissues by mistake. If a person has MG, the antibodies destroy, block, or attack the acetylcholine receptors needed for muscle contraction. As a result, the muscles can’t contract properly and become tired and weak easily.
The thymus gland is a part of the immune system that is situated in the upper chest beneath the breastbone. During infancy, the thymus gland is large and continues to grow until puberty. Later it gets smaller and eventually is replaced with fat. Many people with this disorder have thymus gland conditions that may bring on MG. About two-thirds of young people with MG have overactive thymic cells (thymic hyperplasia). And one in ten people with MG has a benign tumor in the thymus gland.
In rare cases, mothers with MG have children who are born with neonatal myasthenia gravis. When treated on time, children may recover within two months after birth. And few children are born with the congenital myasthenic syndrome (rare), a hereditary form of myasthenia gravis.
Risk factor
Certain factors can worsen myasthenia gravis, it may include:
- Illness or infection
- Surgery
- Medications like quinidine gluconate, quinidine sulfate, quinine phenytoin, and beta-blockers
- Certain anesthetics and some antibiotics
- Pregnancy
- Fatigue
- Stress
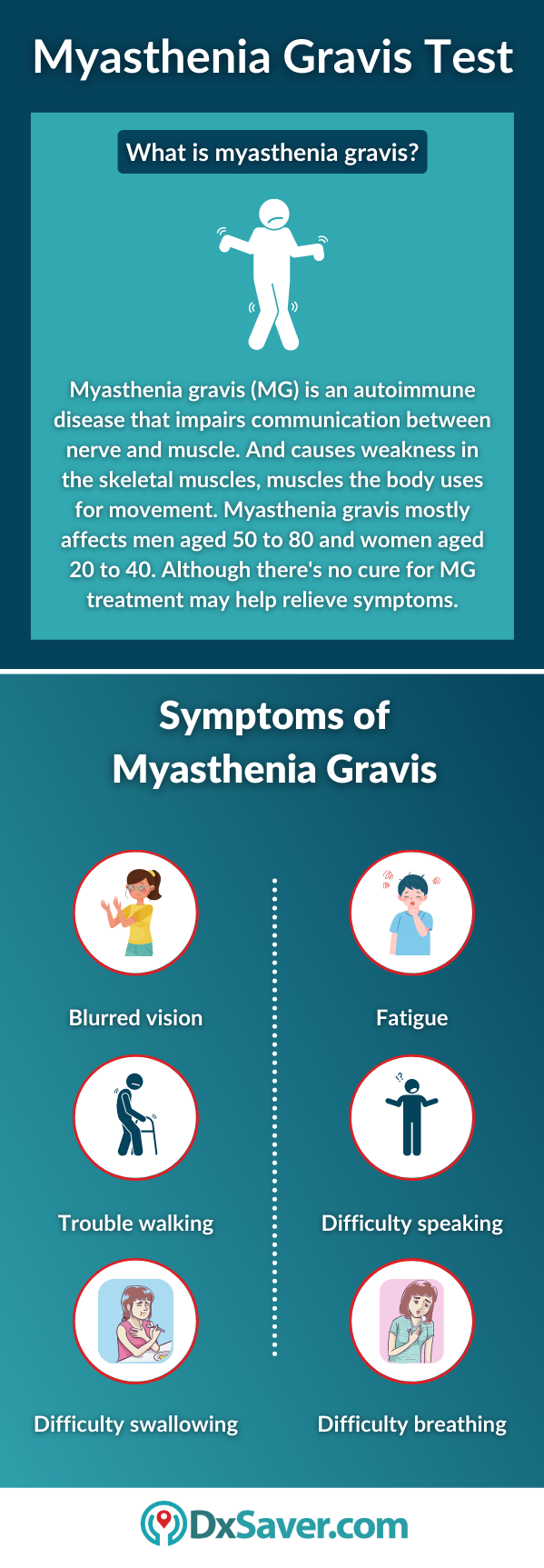
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis
Generally, weakness associated with myasthenia gravis gets worse with more activity and improves with rest. Muscle weakness can come and go. Symptoms of MG progress over time, generally reaching their worst within a few years after the onset of the disease. Initial symptoms of myasthenia gravis often come on suddenly. Usually, the intensity of muscle weakness changes from day to day and many people feel strongest at the start of the day and weakest at the end of the day.
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis may include:
- Blurred or double vision
- Weakness of the eye muscles
- Drooping of eyelids (ptosis)
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty holding up their head or moving their neck up
- Limb weakness
- Trouble walking
- Problems walking upstairs or lifting objects
- Facial paralysis
- Difficulty breathing due to muscle weakness
- Difficulty swallowing or chewing
- Fatigue
- Weakness in the fingers, hands, arms, legs, and neck
- Hoarse voice
Complications
- Myasthenic crisis – This is one of the most dangerous potential complications of MG. It is a life-threatening condition that takes place when the muscles that control breathing become too weak to work. One in five people with MG experiences a myasthenic crisis or severe respiratory muscle weakness. Medications and blood filtering therapies can help people to breathe on their own.
- Thymus gland tumors – Some people with MG have a tumor in the thymus gland and most of these tumors called thymomas are not cancerous. About 20% of people with MG whose symptoms began between the ages of 30 and 60 years have thymoma.
- Underactive or overactive thyroid – The thyroid gland (in the neck) secretes hormones that regulate the metabolism. When the thyroid is underactive, people may have difficulties dealing with cold, weight gain, and other issues. And when it is overactive, the thyroid can cause difficulties dealing with heat, weight loss, and other issues.
Apart from this people with MG are at a higher risk of developing autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis
Doctors will review the symptoms, medical history and conduct a physical examination. A doctor may use several tests. It may include:
- A neurological examination – The physician will check muscle strength and tone, coordination, sense of touch & sight, reflexes, balance and look for impairment of eye movements.
- A blood test – Nearly 85% of people with myasthenia gravis have unusually high levels of acetylcholine receptor antibodies in their blood. And 6% of patients have muscle-specific kinase (MuSK) antibodies. And blood tests can detect this antibody.
- Ice pack test – When a person has a droopy eyelid, doctors place a bag filled with ice on the eyelid. After a few minutes, he/she removes the bag and analyzes the droopy eyelid for signs of improvement.
- Edrophonium test – The doctor injects you with a chemical (edrophonium chloride) to see if it improves muscle strength. When it does, that is a sign you might have myasthenia gravis.
- Single-fiber electromyography (EMG) – A doctor puts a thin wire electrode through the skin and into a muscle. It can test the electrical activity between the brain and muscles.
- Imaging – Imaging of the chest using computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may identify the presence of a thymoma.
- Pulmonary functioning tests – To see if your lungs are affected by myasthenia gravis, doctors test your breathing.
Is myasthenia gravis curable?
Although there is no cure for myasthenia gravis, the symptoms can often be controlled. Detecting early is the key to managing the condition. Treatment for MG aims to increase muscle function and to prevent swallowing & breathing problems. Many individuals with MG have good results from treatment. For some individuals, MG may go into remission for a while and muscle weakness may go away completely. Rarely, people may go into remission or improve without treatment.
Treatment for myasthenia gravis
Treatment aims to manage symptoms and control the activity of the immune system. It may include:
- Medications – Immunosuppressants and corticosteroids are used to suppress the immune system. It can help minimize the abnormal immune response that occurs in MG. And cholinesterase inhibitor like pyridostigmine is used to increase communication between nerves & muscles.
- Plasma exchange (plasmapheresis) – This is a process that removes harmful antibodies from the blood. This may result in an improvement in muscle strength. It is a short-term treatment. Plasmapheresis is helpful before surgery or during times of extreme MG weakness. However, the body continues to produce harmful antibodies and weakness may recur.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) – This therapy injects new antibodies into the bloodstream. These antibodies alter the immune system response to help with symptoms. Usually, benefits are seen in less than a week and can last 3 to 6 weeks. Side effects may include chills, dizziness, headaches, and fluid retention.
- Monoclonal antibodies – Rituximab and eculizumab are intravenous medications for myasthenia gravis. Usually, these drugs are used for people who don’t respond to other treatments and can have serious side effects.
- Surgery – Some people with MG have a tumor in the thymus gland. A thymectomy, surgery to remove the thymus gland can help reduce symptoms. Surgical removal sometimes improves symptoms, even when tests don’t show a problem with the thymus gland.
Lifestyle changes
There are no preventive measures to prevent MG, as the exact cause of this autoimmune reaction is unclear to scientists. However, there are certain things you can do at home to help alleviate symptoms of MG:
- Take naps or rest breaks throughout the day to help minimize muscle weakness.
- Don’t become too cold or overheated.
- Avoid stress and heat exposure (they can worsen symptoms).
- Apply cold compresses on the forehead and neck when you feel overheated.
- Adjust your eating routine by trying to eat when you have good muscle strength.
- Take a break between bites of food and take time chewing the food.
- Get plenty of carbohydrates and protein in your diet for energy.
Provider locations
Myasthenia gravis test can be done in any of the following locations by visiting the lab near you. To know the myasthenia gravis test cost, refer to the first section of the article.
- Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Hawaii
- Georgia
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Puerto Rico
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Frequently Asked Questions
Will insurance cover my testing cost?
No, insurance will not be covered in the billing. However, they will provide you with a receipt for insurance reimbursement purposes.
How should I book my appointment?
You can choose the most suitable provider from above and make an appointment by following the instructions mentioned by them.
Can I cancel my lab test order?
Yes, you can cancel your lab test order any time before your testing. A refund will be initiated after deducting the cancellation fee. However, cancellation is at the discretion of the provider.
Do the providers offer result interpretations?
Yes, a few providers may provide doctor consultation who will take you through the results and provide clarification if needed.
How do I receive my report?
To ensure your privacy, the test report will be mailed to you by the provider.
Other topics you may also be interested in:-
- Zika Virus Test Cost in the US
- ALT Blood Testing the US
- Symptoms of Oral Herpes
- What is a Titer Test?
- Importance of Aldosterone to Renin Ratio
- Liver Health and AST Levels
- Ammonia Testing Cost in the US
- Symptoms of Lactose Intolerance
- Importance of Occult Blood Test
- Rhemunotaid Arthritis Causes and Symptoms
- Signs of Perimenopause in Women
- Difference Between COVID and Flu
- Food Sensitivity Test Cost in the US
- Physical Fitness Check
- Symptoms of Ovulations and Testing Cost
- Pregnancy Qualitative Blood Testing in the US
- Oral HPV Symptoms in Men and Women





